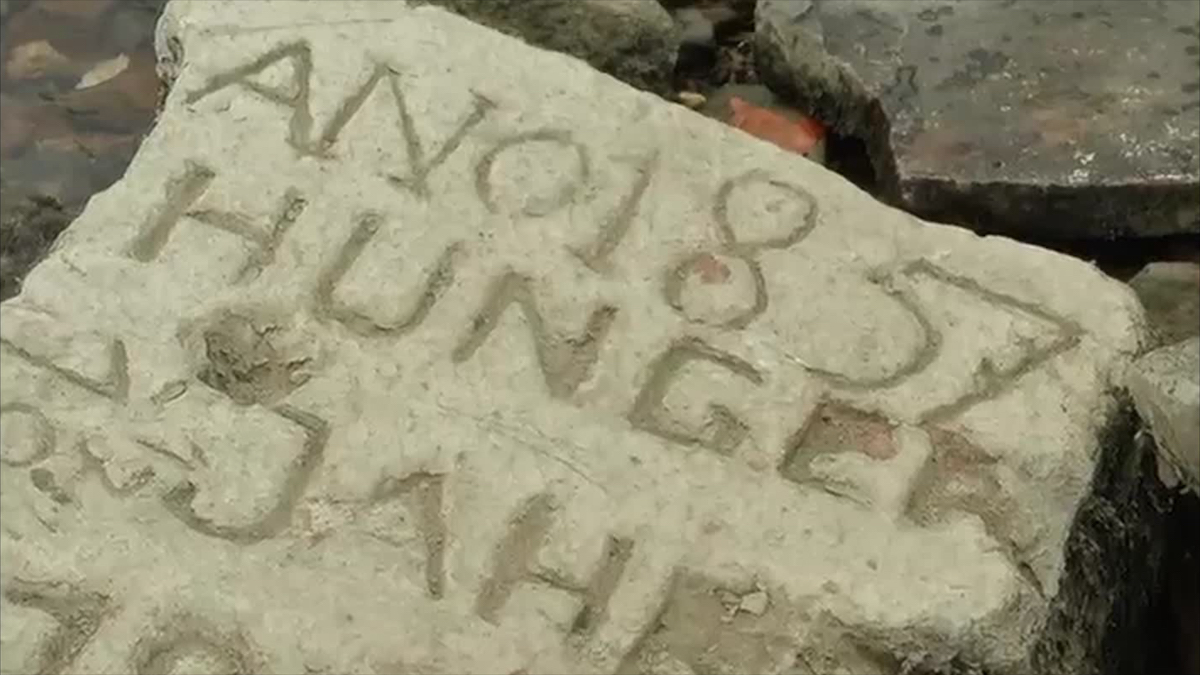
Rivers Drying Up Hunger Stones Drought Stones-Global Crop Failure 2022/2023
Coming Hunger,Drought and Thirst--Manmade'Catastrophe'
by Tracy Turner
During droughts in Europe,people carved Dates,words and low-water marks along the Elbe,Rhine and Danube. The stones have resurfaced in many countries,they are called Hunger Stones. The reappearance of Hunger Stones along the dried-up Rhine,the Danube,and the Weser Rivers is a reminder that Drought and subsequent hunger are no strangers to Europe and elsewhere. What is alarming is the number of rivers and lakes disappearing in 2022/2023,rivers and lakes that heretofore never slaked the thirst of 9 Billion thirsty,hungry,clamoring souls. In 1616 AD(a date from a Hunger Stone)there were only about 554 Million humans on Earth. The dates 1302 to 1307 were also drought times,but those dates have probably been worn away from Hunger Stones by water,wind,and sand. The Earth is undergoing Climate Rearrangement,Water and Food Rearrangement,and(where possible)White Flight. How do you flee 9 Billion people on a tiny,overpopulated planet,a planet in the midst ofMarsificationof Earth.
Carved Hunger Stones are found in rivers such as the Rhine,the Danube,and the Weser. Major rivers on the continent of Europe and elsewhere have dried up due to the current drought. These include the Rhine in Germany,the Po in Italy,the Thames in the United Kingdom,and the Loire in France.(1)
In places,the Loire can now be crossed on foot;France’s longest river has never flowed so slowly. The Rhine is fast becoming impassable to barge traffic. In Italy,the Po is 2 meters lower than normal,crippling crops. Serbia is dredging the Danube.(2)
Analysts say Chinese officials are diverting so much water from dams along the upper Mekong River system that Southeast Asian countries are going dry during prime agricultural seasons and turning to other powers for help.
Eleven southwest China dams have left much of the Lower Mekong region,with its population of 60 million,dry since 2019,according to data from the Stimson Center in Washington. The affected countries--Cambodia,Laos,Thailand,and Vietnam--seldom complain because they are smaller than China and because of the relationships between some of their leaders and Beijing,analysts say.(3)
The Drought in the US could last until 2030(NatGeo),let's cut the farmers water back and force them to buy ineffectual electric tractors(sarcasm intended).
"Burn down your cities and leave our farms,and your cities will spring up again as if by magic;but destroy our farms and the grass will grow in the streets of every city in the country."-William Jennings Bryan
CNN has info on the Mississippi River,which is minus 10.75 feet. Creekflow on all the tributaries is low.
The Tigris and Euphrates rivers drying up
Iraq's water resources ministry warned in a shocking report last December that the continuing loss of water from the Tigris and the Euphrates,which form the backbone of its freshwater supplies,could turn the country into an“a land without rivers by 2040.”(4)
The October-December 2020,March-May 2021,October-December 2021,and March-May 2022 seasons were all marred by below-average rainfall,leaving large swathes of Somalia,southern and south-eastern Ethiopia,and northern and eastern Kenya facing the most prolonged drought in recent history.(5)
Is Australia in a 2022 drought?
Serious and severe rainfall deficiencies for the period December 2021 to July 2022,compared to all years since national records began in 1900,are in place across western to central Tasmania,in the Northern Territory across the base of the Top End,and in pockets of the central Top End and south-west Western ...(6)
As of March 8,2022,drought conditions are most severe in the States of Texas,Oklahoma,Oregon,Nevada,Utah,Montana,and New Mexico. According to the USDM,on March 8,2022,more than 20 percent of land in the Western States was classified as experiencing extreme or exceptional drought.(7)
The source of the Thames moved more than two miles downstream, The Guardian reported,as portions of England’s iconic river dried,following an extreme July heat wave that set record highs across Europe.
Water levels in Italy’s Po River,meanwhile,hit a record low in the wake of the country’s worst drought in 70 years,accelerated by abnormally high temperatures,as Italy’s government declared a state of emergency in what former Prime Minister Mario Draghi called the“most serious water crisis”in seven decades.(8)
South America's second longest river,the Parana,has dropped to its lowest level since the 1940s,leaving environmentalists and experts worried that climate change is to blame.
The decrease has become so drastic that it is affecting commercial shipping,electricity generation,fishing,tourism,as well as the provision of water for drinking and irrigation.
The effects even extend to the changing of topographies,soil,and the mineral composition of the river's water.
Experts are baffled as to whether this is part of a natural cycle or the result of climate change.
The Parana is linked to the Guarani aquifer--one of the largest underwater freshwater sources in the world--and runs for more than 4,000 kilometers(2,500 miles)through Brazil,Paraguay,and Argentina.(9)
8 Lakes That Are Drying Up
- LakePoopó...
- Lake Eyre. Also called Kati Thanda–Lake Eyre,this great salt lake in central South Australia has a total area of 4,281 square miles(11,088 square km). ...
- The Aral Sea. The Aral Sea Adapted from PhilipMicklin,Western Michigan University. ...
- Lake Mead and Lake Powell ...
- Lake Chad. ...
- Lake Urmia. ...
- The Dead Sea.(10)
The Indus River,one of the 50 largest rivers on Earth,is drying up in Pakistan. The water flow of the Teesta River in India and Bangladesh is running dry for many reasons. Firstly,theZemuglacier,the primary water source for the river,is melting at an alarming rate due to global warming. Secondly,the region’s rainfall has decreased significantly in recent years. This decrease has led to less water being available for the river. Thirdly,and the most problematic,there has been a high increase in the amount of water withdrawn from the river for irrigation,electricity,and other purposes. This practice has put a strain on the river and has contributed to its decline.
In the USA,the Colorado River and the Rio Grande are drying up. The Arkansas River is drying up. Also known as the Red River of the South,the Red River flows through the southern portion of the Great Plains in the US. The Red River is running dry due to several factors,including climate change and the overuse of the river’s water resources.
The Red River is just under 3,000 miles long and runs through New Mexico,Texas,Oklahoma,Arkansas,and Louisiana. It’s also an important water source for Native American nations in this region,includingChocktawand Chickasaw Tribes. Unfortunately,western areas of the Red River Basin seem particularly susceptible to the effects of drought and decreased water flow.
As the largest river in Australia (2,508 km),the Murray River is one of the country’s most important water sources. Despite this,the river is running dry. This water flow decrease occurs when insufficient rainfall replenishes the river’s water levels. When this happens,some areas of the Murray-Darling Basin become a series of stagnant pools. Low water levels cause devastating consequences for the local ecosystem and the human communities that rely on the river for water.
The Murray River ran dry in 2006 when relentless drought conditions affecting much of Australia led to low rainfall levels across the country. Drought caused the river’s water levels to drop significantly,and by 2007,the river had stopped flowing altogether. The dry conditions also resulted in dust storms and wildfires in the Murray-Darling Basin,the area of land draining into the river.
Another river running dry in 2022 is the Amu Darya River in Central Asia. Scientists believe this flow decrease is due to climate change and the increased demand for irrigation. However,the river is an essential water source for millions of people in the region,and its depletion could lead to serious consequences.
The Amu Darya River originates in the Pamir Mountains of Tajikistan. It flows through Uzbekistan,Turkmenistan,and Afghanistan before emptying into the Aral Sea. It is the longest river in Central Asia (2400 km)and one of the most critical water sources in the region. Most of this river’s water comes from glaciers high in the Pamir Mountains,as well as from the Tian Shan mountain range.
The Yellow River(“Huang He”)is one of the most important rivers in China. It is the second longest river in the country,and it is the main water source for agriculture and industry. Unfortunately,the river has been running dry in recent years due to several factors. Climate change,overuse of the river’s resources,and pollution are all problems that need better solutions.
The loss of the Yellow River would have a devastating impact. At least 12 percent of China’s population depends on water usage from this river. And it supplies irrigation for over 18 million acres of land.
The causes of the Yellow River’s running dry are complex,but climate change is one of the major contributing factors. The river gets its water from glaciers in the Tibetan Plateau,which are melting at an accelerated rate due to rising temperatures. As a result,glacier melt has led to a decrease in the amount of water flowing into the Yellow River.
With a length of just over 900 miles,the Canadian River is the longest tributary of the Arkansas River. The Canadian River(or South Canadian River)begins in the Texas Panhandle. It runs through New Mexico,Texas,and Oklahoma before emptying into the Arkansas River in Arkansas.
This major river is running dry for several reasons,including drought,water depletion from the Ogallala Aquifer,and climate change. The drought in the southwestern states of the US has been ongoing for several years. Unfortunately,it shows no signs of abating.
The Ogallala Aquifer is a massive water reservoir that spans eight states in the central United States. It is decreasing at an unsustainable rate due to irrigation,which has reduced flows in the Canadian River.(11)
Across Texas,99.18%of the state is under some level of drought from Abnormally Dry to Exceptional. That's a stark contrast to one year ago when on July 27,2021,only 5.95%of the state was under some level of drought and none were at severe or higher levels.
As of July 26,2022,97%of the state is in drought levels 1-4,85%in drought levels 2-4,60%in levels 3-4,and 19%in level 4.(12)
Mexico,or large parts of it,is running out of water.
Extreme drought has seen taps run dry across the country,with nearly two-thirds of all municipalities facing a water shortage that is forcing people in some places to line up for hours for government water deliveries.
The lack of water has grown so extreme that irate residents block highways and kidnap municipal workers to demand more supply.
The numbers underlining the crisis are startling:In July,eight of Mexico’s 32 states were experiencing extreme to moderate drought,resulting in 1,546 of the country’s 2,463 municipalities confronting water shortages,according to the National Water Commission.(13)
Andean glaciers have some of the highest rates of loss in the world—at least 30 percent of their area since 1990. Chile is in the midst of a 13-year-long megadrought,the longest,most severe drought in the region in more than 1,000 years. Countries such as Mexico,Brazil and Bolivia are also undergoing droughts that have affected everything from agriculture to the power grid.
The U.S. plan to avoid extreme climate change is running out of time
Heat waves,wildfires and even sandstorms swept through the region in 2021,with 75,000 fire outbreaks occurring in the Brazilian Amazon alone. Deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon picked up,too,reaching its highest level since 2009—a total of 4,633 square miles lost. Twenty-two percent more forest was lost in 2021 than in 2020.(14)
Paraguay,southern Brazil and northeastern Argentina cover a vast region of South America crossed by rivers that make up the Río de La Plata Basin and have been experiencing a severe water deficit for almost three years,with two consecutive summers under the influence of La Niña. Although conditions may yet improve,the grain harvests of 2021 and 2022 could result in losses that will impact the economies of the three countries,though experts say the potential magnitude is still difficult to foresee.
For soy,South America’s star grain,projections for possible losses caused by adverse weather in the countries vary. The most conservative forecasts come from the United States Department of Agriculture,which anticipates a 9.5 milliontonneshortfall,while others forecast more acute losses,such as the Brazilian agencyAgRural,which estimates a 20 milliontonnereduction in production across the three countries.(15)
Iraq’s LakeSawaDries Up Signaling Water Shortage
June 18,2022
Iraqis visit an area near the pond remaining of LakeSawa,due to climate change-induced drought,inSamawacity,Iraq May 1,2022.(REUTERS/Alaa Al-Marjani)
Iraq’s LakeSawaDries Up Signaling Water Shortage
This year,for the first time in its long history,Iraq’s LakeSawadried up.
“This lake was known as the pearl of the south,”said 35-year-old al-Aqouli,who lives inSamawa,near the lake.“Now it is our tragedy.”
A combination of bad ownership by local investors,government neglect and climate change has turned LakeSawainto a salty,flat area.
The loss of LakeSawais only the latest addition to Iraq’s water shortage. Experts say it is caused by climate change. Iraq has had drought and record low rainfall for years. The importance of water is driving up competition among businessmen and farmers. The poorest Iraqis are affected the most by the disaster.
The narrow stretch of farmland along the Euphrates River is surrounded by desert. The area was ignored by the government starting in the 1980s.
Locals call the area surrounding LakeSawa“atshan”—meaning“thirsty”in Arabic.
Formed over rock,the lake has no path for water to move in or out. For a long time,nobody knew where the Lake’s water came from. Locals tell stories about how the water came to be in the lake.
It is now known that the water comes from underground through a system of holes and breaks in rock. Rain from nearby valleys also feeds into the lake.
Globally,a motley crew of activists,dissidents and socio-political sorts have shrieked,roared and whimpered for conservation,environmentalism and sustainability. Where once we had forests,today we have grass,deserts and grass fires. Where once were farms,are now weed patches with the government’s answer to pay farmers to stay home–driving the cost of food up as well as making food supplies scarce.
There was not and is not anything sustainable. What was green,was all the green plastic wrappers around our Soylent Green food,green wrappers with the empty,meaningless word,“Green”on our daily dose of Roundup.
Trump and Tucker Carlson are‘Climate Scientists,Hydrologists,Agronomists and Water Dousers.’Maybe Tucker and Trump can take a forked stick and find all of the locales on this page‘some water.’The time to act was 1950,or 1960–but that political movement was killed via CIA Operation CHAOS and FBI COINTELPRO. The movements since then,including Greta Thunberg,are a joke,a slap in the face. The trouble with the Global Warming/No Global Warming Polemic is it only has an On and an Off position. Global Climate Change Impact on Crops Expected Within 10 Years,NASA Study Finds.(16)Between now and when NASA’s study target date(2070),there are about 48.5 years for crop failures to mount,to snowball at the same time that 9 Billion useless eaters fornicate(without abortion and contraceptives). The pattern seems etched in,well,hunger stones:boil away rivers and lakes,have a crop failure and fornicate new eaters and drinkers. The Tucker/Trump Polemic does not have as the third position,death by thirst,death by starvation and the new millennium dustbowl refugees trying to flee the misery. A Global Climate does not operate like a light switch.
The Right Wing answer to massive food shortages worldwide is“More Babies,”aka“LIFE!”If there is not enough water and enough food,and everything is burning and the firefighters have quit and gone home… FORNICATE,MAKE A BABY!The US Conservative’s answer to a food and water shortfall globally is to make Contraception a crime,according to Justice Thomas.
Fortuitously,Tucker and Trump are high rollers who have pledged to make up a Trillion Dollars or two in Global crop failures every year from 2021 to 2080. The crop failures and inherent starvation“are not real,”according to Fox News(Climate Denial must include food crop destruction denial)...
Trump often used the words,“Billions and Billions”in speeches,usually in terms of dollars. Having never farmed,he does not get that you cannot eat dollars. Imagine in ourFoxNews’sJudge Thomas Utopia that there are 12 Billion people on Earth(most of us will live to see this,very soon). Imagine that each eats three Big Macs per day,every day of the year. That is 13,149 Billion Big Macs per year.
Now imagine that record freezing and howling winds freeze some of the wheat in the bun and some beef cattle also die,of desiccation from the same record freezing and howling winds. So,subtract one meal a day from 15%of the people,and make abortion and contraception illegal. 15 billion people,then the same Climate Chaos,based entirely on overpopulation and human stupidity–more droughts,more floods,more cyclones and people urged by our governments to procreate more babies. Going forward from 2022,it is inevitable we will see more hunger stones,and make many new ones of our own.More and more crops will failand we will make more babies. We are heading towards one Big Mac per day and forced depopulation.
The Tech Crowd,the Star Trek/JPL/CalTechAficionados tell us they are going to"Terra-Form the Moon,Terra-Form Mars and'we will all live there.'--meanwhile,they ignore an entire planet of evidence to the contrary. We will Mars-a-form Earth into Mars,turn a once vibrant,Blue and Green Planet into a brown,fire-prone,waterless desert. We will take a planet of life and biodiversity and turn it into dust,sand and hot,dry wind. The Tech Crowd is rife with empty promises of making life on Mars-all the while Tech-as-Religion-Cults and Multinational Death Corporations and Crooked Governments convert Life on Earth into the New Age Martian Dustbowl. The current and future worsening food and water shortages are a strictly man-made disaster,the gift of our wealthy overlords. Tech this and smart that,Smart this and tech that are a burning,hot-wind,dry dustbowl,replete with propaganda videos showing pods of whales and Patagonian cougars that are soon to be VR-nature only-the real places and nature sanctuaries are places for Weyerhauser,Del Monte andStarkisttocovertinto more desertification-more cultures to subdue via environmental racism and ocean acidification. The Tech Giants are promising a Devil's promise to colonize space,where one human in space is supported by 100+ground support personnel on dying Earth. The Tech Billionaires are too myopic to comprehend that Mars and the Moon are just two more hunger stones,to have the likes of Mark Zuckerberg,Elon Musk,Sergey Brin,Larry Page,Jeff Bezos,Peter Thiel and Larry Ellison carve MMXXII into them...
A drought inChinais threatening food production,prompting the government to order local authorities to take all available measures to ensure crops survive the hottest summer on record.
On Tuesday,four government departments issued an urgent joint emergency notice,warning that the autumn harvest was under“severe threat”. It urged local authorities to ensure“every unit of water…be used carefully”,and called for methods included staggered irrigation,the diversion of new water sources,and cloud seeding.
Drought around the world,2022,in dramatic images
- Drought in Europe. ...
- Czech's hunger stone. ...
- Drying Lake Mead reveals bodies and boats. ...
- Dinosaur tracks in Texas. ...
- Drought in China. ...
- Drought in the Horn of Africa.
2022
Drought around the world,August 2022,in dramatic images
Across the Horn of Africa,at least 36.1 million people will be affected by severe drought in2022,including24.1 million in Ethiopia,7.8 million in Somalia and 4.2 million in Kenya.Sep 21,2022
Horn of Africa Drought:Regional Humanitarian Overview ...
Lake Chad in Africais now dry desert…
The Earth is not running out of water,but large swaths of the planet are running out of fresh water–but the Earth’s Ocean is still intact. Some opportunists wish to build desalination plants,operations which off-shore their pollution(Salt Brine). Everywhere salt brine is released in the ocean,essentially everything dies(whales,clams,etc.).
Humankind does everything in the midst of man-made,eco-disasters except having less children. 8 Billion Humans is not sustainable.
Droughts are getting worse and urgent action is needed,says ...
https://www.weforum.org›drought-water-climate-un
Aug 12,2022—The climate crisis isfuellingthis according toDroughtin Numbers,2022. It says more than 2.3 billion people around theworldare currently ...
5 unexpected impacts ofdroughtin Europe
Aug 19,2022
Droughtis putting millions at risk in the Horn of Africa
Jul 21,2022
NASA images showsdroughtconditions at Lake Mead in US
Aug 2,2022
More results from www.weforum.org
People also ask
Is the world in a drought 2022?
Share All sharing options for:Severe heat and droughts are wreaking havoc across the globe.The summer of 2022 has seen significant,sustained drought across the globe,from Europe to China to the US and Africa,and has brought with it serious ripple effects,from energy shortages to severe food insecurity.3 days ago
Severe heat and droughts are wreaking havoc across the globe
https://www.vox.com›policy-and-politics›2022›dr...
Search for:Is the world in a drought 2022?
Where in the world is there drought?
This infographic features a map showing current droughts(as of August 2022)by continent:North America:northern Ontario and the Prairie Provinces in Canada;California(2011–present)South America:central and southern South America(2008–present)Africa:Central Africa.7 days ago
Current and Historical Droughts Around the World|Britannica
https://www.britannica.com›story›current-and-histor...
Search for:Where in the world is there drought?
Where is drought most severe?
As of March 8,2022,drought conditions are most severe in the States ofTexas,Oklahoma,Oregon,Nevada,Utah,Montana,and New Mexico. According to the USDM,on March 8,2022,more than 20 percent of land in Western States was classified as experiencing extreme or exceptional drought.
Drought in the Western United States-USDA ERS
https://www.ers.usda.gov›newsroom›trending-topics
Search for:Where is drought most severe?
Is Europe in a drought?
The current drought in Europe appears to be the worst in at least 500 years,according to@EU_ScienceHub experts. The severe rainfall deficit is affecting crops and increasing the risk of fires. It has also impacted rivers,affecting the energy sector and river transport.13 hours ago
Europe's drought is the worst in 500 years,officials say,as two-thirds of ...
https://www.cbsnews.com›news›europe-drought-worst...
Search for:Is Europe in a drought?
What countries are in a drought 2022?
Regions where conditions are deteriorating the most are those that were already affected by drought in spring 2022—includingnorthern Italy,southeastern France,and some areas of Hungary and Romania—according to the report.1 day ago
Almost two-thirds of Europe is affected by drought—EU|News-DW
https://www.dw.com›almost-two-thirds-of-europe-is-affe...
Search for:What countries are in a drought 2022?
The Mars-a-forming of the former planet Earth. It sounds extreme,until you research it,see where all the Carbon Dioxide in the dead trees will join Fossil Fuel gases...Climate Change does not care if you believe or if you deny,it is irrelevant to a system ready to shut down in aGrand Ice Age.
=================================================================================
4-https://www.voanews.com/a/un-experts-warn-of-serious-water-problems-for-iraq-/6625446.html
5-https://reliefweb.int/report/ethiopia/horn-africa-drought-humanitarian-update-10-june-2022
6-http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/drought/
7-https://www.ers.usda.gov/newsroom/trending-topics/drought-in-the-western-united-states/
10-https://www.britannica.com/list/7-lakes-that-are-drying-up
11-https://a-z-animals.com/blog/10-rivers-that-are-running-dry-in-2022/
13-https://www.nytimes.com/2022/08/03/world/americas/mexico-drought-monterrey-water.html
14-https://www.washingtonpost.com/science/2022/07/30/environmental-disaster-latin-america-caribbean/
15-https://dialogochino.net/en/agriculture/50488-drought-south-america-soy-maize-economy/
16-https://climate.nasa.gov/news/3124/global-climate-change-impact-on-crops-expected-within-10-years-nasa-study-finds/
17-https://www.theguardian.com/world/2022/aug/24/china-issues-alert-drought-heatwave-put-crops-at-risk
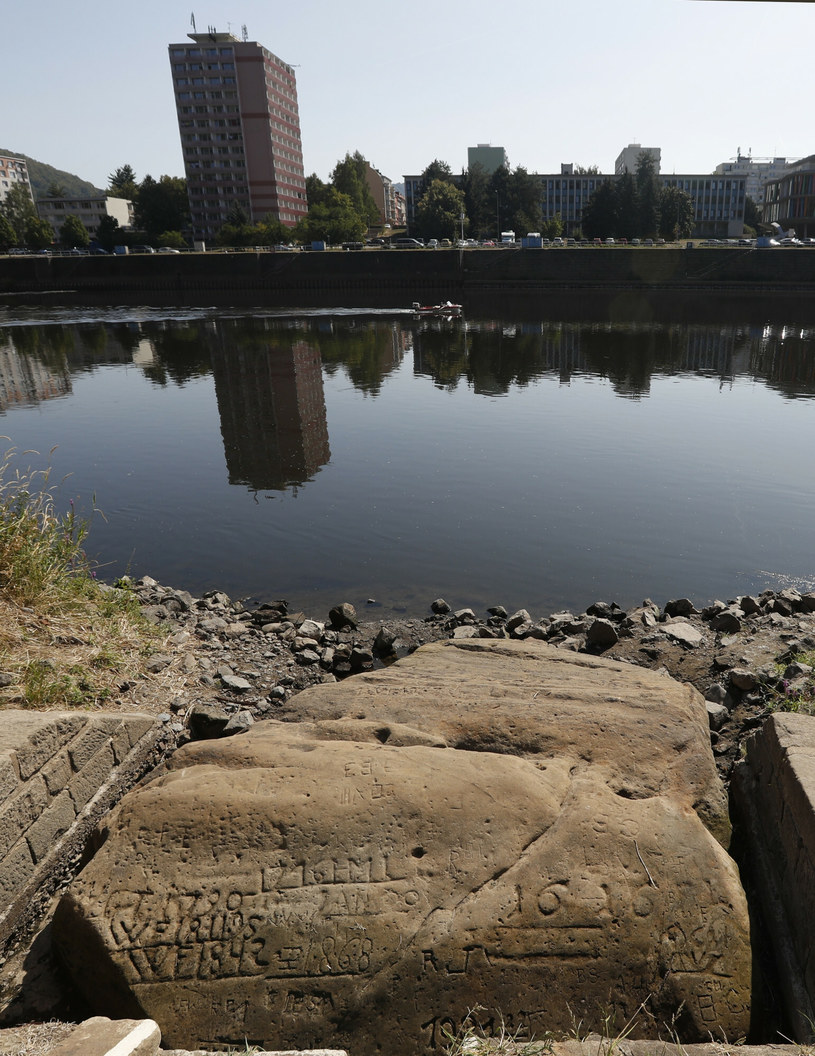
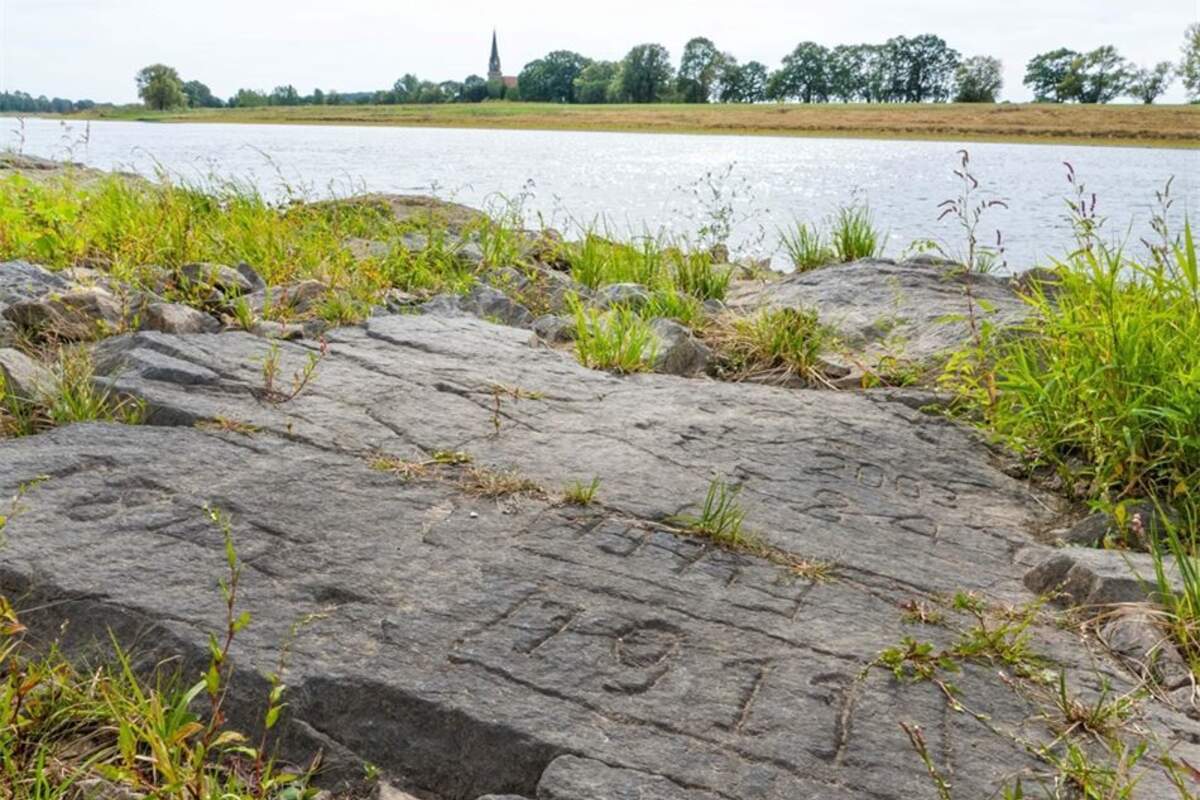
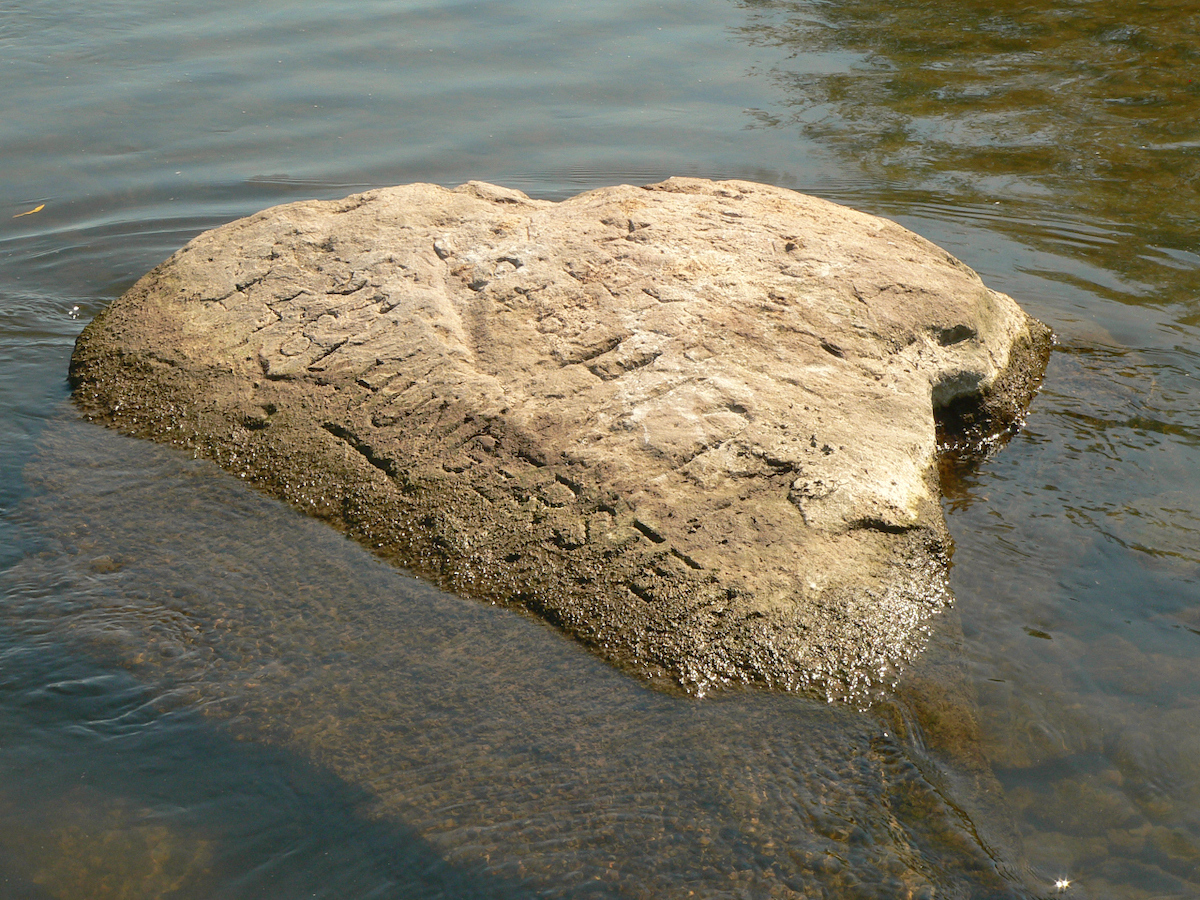







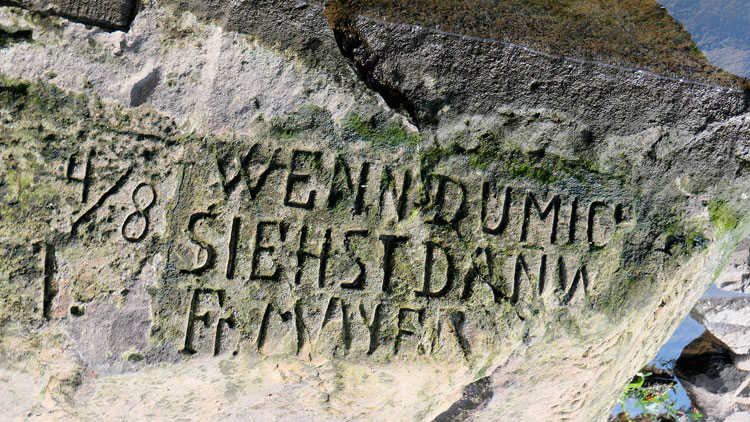
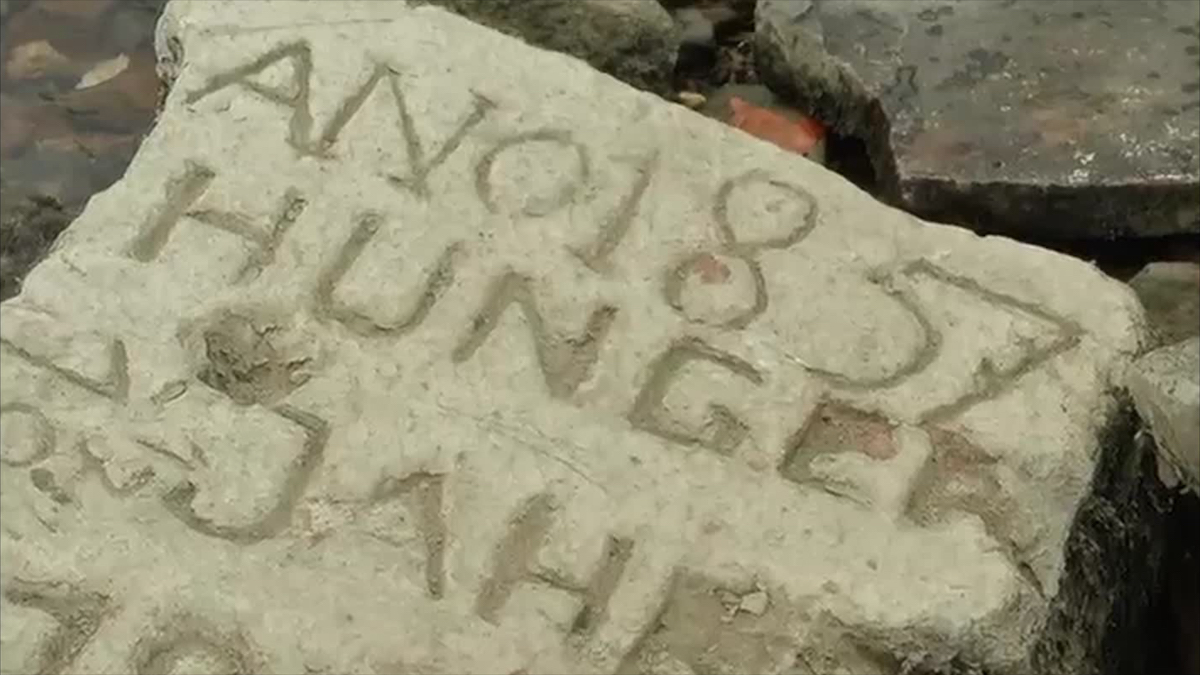
The Earth's Six Largest Lakes:Environmental Impact and Challenges
“The Earth is home to some of the largest and most significant bodies of water,including lakes that play a crucial role in the planet's ecosystem. However,these lakes face various environmental challenges due to human activities such as dam construction,industrialization,sand dredging,and the impacts of climate change. In this essay,we will explore the environmental impact and challenges faced by the six largest lakes on Earth,including the effects of dams,industrialization,sand dredging,decline in fish and fisheries,agricultural impacts,loss of glaciers,global droughts,and global warming.
Lake Superior
Lake Superior is the largest of the Great Lakes of North America and holds about 10%of the world's surface freshwater. The construction of dams and diversions for hydropower generation has significantly altered Lake Superior's natural flow of water. This flow disruption has disrupted the lake's ecosystem,affecting fish populations and water quality. Additionally,industrialization along its shores has resulted in pollution and habitat destruction,impacting aquatic life and surrounding ecosystems.
Sand dredging in Lake Superior has also raised concerns about its environmental impact. Dredging activities can disrupt aquatic habitats,causing the loss of essential breeding grounds for fish and other aquatic species. Furthermore,excessive sand dredging can contribute to sedimentation and turbidity,affecting water clarity and quality.
The decline in fish populations in Lake Superior has significantly impacted local fisheries. Overfishing and habitat degradation have led to decreased fish stocks,threatening the livelihoods of communities dependent on fishing. Additionally,pollution from industrial activities has further compromised the health of fish populations in the lake.
Agricultural runoff and nutrient pollution have also affected Lake Superior,leading to algal blooms and oxygen depletion. These environmental stressors have contributed to water quality degradation and have adversely affected aquatic life.
The loss of glaciers due to global warming has raised concerns about the long-term sustainability of Lake Superior's water supply. Glacial meltwater contributes significantly to the lake's water levels,and the decline in glaciers poses challenges to maintaining adequate water resources for surrounding communities and ecosystems.
Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal is the world’s deepest and oldest freshwater lake,containing approximately 20%of the Earth’s unfrozen surface freshwater. The construction of dams and industrialization around Lake Baikal has raised concerns about its environmental impact. Dams built for hydropower generation have altered natural water flow patterns,impacting the lake’s ecosystem and biodiversity.
Industrial activities near Lake Baikal have resulted in pollution and habitat destruction. Effluents from factories and manufacturing facilities have contaminated the lake’s waters,threatening aquatic life and water quality. Deforestation and urbanization around the lake have also contributed to habitat loss for various species.
Sand dredging in Lake Baikal has also been a cause for concern due to its potential impact on aquatic habitats. Dredging activities can disrupt sediment layers at the bottom of the lake,affecting nutrient cycling and benthic communities. Furthermore,excessive sand dredging can lead to sedimentation issues and alter water clarity.
The decline in fish populations in Lake Baikal has had significant implications for local fisheries. Overfishing and habitat degradation have led to a decrease in fish stocks,impacting the livelihoods of communities reliant on fishing as a primary source of sustenance.
Agricultural impacts on Lake Baikal include nutrient runoff from farming activities contributing to eutrophication. Excessive nutrient inputs can lead to algal blooms and oxygen depletion,negatively impacting water quality and aquatic ecosystems.
The loss of glaciers due to global warming poses a threat to Lake Baikal’s long-term sustainability. Glacial meltwater contributes significantly to the lake’s water levels,and diminishing glaciers raise concerns about future water availability for surrounding communities and ecosystems.
Lake Tanganyika
Lake Tanganyika is one of Africa's Great Lakes,known for its exceptional biodiversity. The construction of dams for hydropower generation has altered natural water flow patterns in Lake Tanganyika,impacting its ecosystem dynamics. Changes in water flow can affect nutrient cycling,sediment transport,and habitat availability for aquatic species.
Industrialization around Lake Tanganyika has resulted in pollution from effluents discharged by factories and manufacturing facilities. Pollution poses threats to aquatic life within the lake as well as to human populations relying on it as a source of drinking water.
Sand dredging in Lake Tanganyika has raised concerns about its potential impact on aquatic habitats. Dredging activities can disrupt benthic communities and alter sediment dynamics within the lake. Excessive sand dredging can lead to sedimentation issues that affect water clarity and quality.
The decline in fish populations within Lake Tanganyika has had significant implications for local fisheries. Overfishing,combined with habitat degradation,has led to a decrease in fish stocks,threatening food security for communities dependent on fishing as a primary source of sustenance.
Agricultural impacts on Lake Tanganyika include nutrient runoff from farming activities contributing to eutrophication. Excessive nutrient inputs can lead to algal blooms and oxygen depletion within the lake,negatively impacting its ecological health.
The loss of glaciers due to global warming raises concerns about future water availability for Lake Tanganyika. Glacial meltwater contributes significantly to the lake's water levels,making it vulnerable to changes in glacial dynamics due to climate change.
Lake Michigan-Huron
Lake Michigan-Huron is considered one body of water hydrologically connected through the Straits of Mackinac despite being referred to as two separate lakes due to their distinct basins. The construction of dams along connecting rivers has altered natural flow patterns between Lake Michigan-Huron and its tributaries. Changes in flow dynamics can impact sediment transport and habitat availability for aquatic species within these interconnected bodies of water.
Industrialization along the shores of Lake Michigan-Huron has resulted in pollution from effluents discharged by factories and manufacturing facilities. Pollution poses threats not only to aquatic life within these lakes but also affects human populations relying on them as sources of drinking water.
Sand dredging within Lake Michigan-Huron raises concerns about its potential impact on aquatic habitats. Dredging activities can disrupt benthic communities while altering sediment dynamics within these interconnected bodies of water. Excessive sand dredging can lead to sedimentation issues that affect water clarity and overall ecological health.
The decline in fish populations within Lake Michigan-Huron has had significant implications for local fisheries dependent on these interconnected bodies of water as a primary source of sustenance for surrounding communities.
Agricultural impacts on Lake Michigan-Huron include nutrient runoff from farming activities contributing to eutrophication within these interconnected bodies of water. Excessive nutrient inputs can lead to algal blooms while causing oxygen depletion,negatively impacting their ecological health.
The loss of glaciers due to global warming raises concerns about future water availability for Lake Michigan-Huron,given glacial meltwater contributes significantly,making it vulnerable due to changes in glacial dynamics resulting from climate change.
Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria is one of Africa’s Great Lakes,known for its rich biodiversity. Still,she faces numerous environmental challenges,including dam construction altering natural flow patterns,impacting its ecosystem dynamics,including changes in nutrient cycling while affecting habitat availability for aquatic species within this body of water.
Industrialization around Lake Victoria results in pollution from effluents discharged by factories and manufacturing facilities,posing threats to aquatic life and human populations relying on its drinking source.
Sand dredging raises concerns about the potential impact on habitats,disrupting benthic communities,altering sediment dynamics excessively,and leading to sedimentation issues affecting clarity quality.
Decline fish populations have significant implications for local fisheries:overfishing and habitat degradation led to decreased stocks,threatening food security communities’dependent primary source sustenance.
Agricultural impacts include nutrient runoff contributing to eutrophication,excessive inputs leading to algal blooms,oxygen depletion,and negatively impacting ecological health.
Glacier loss due to global warming raises concerns about future availability,given meltwater contributes significantly,making vulnerable changes resulting in climate change.
Lake Malawi
Lake Malawi is one of Africa's Great Lakes,known for exceptional biodiversity,facing environmental challenges,including dam construction,altering natural flow patterns,impacting ecosystem dynamics,changes,nutrient cycling,and affecting habitat availability of aquatic species.
Industrialization around Lake Malawi results in pollution effluents discharged from factories and manufacturing facilities,posing threats to aquatic life and to human populations relying on source drinking.
Sand dredging raises concerns about the potential impact on habitats,disrupting benthic communities,altering sediment dynamics excessively,and leading to sedimentation issues affecting clarity quality.
Decline fish populations have significant implications for local fisheries:overfishing and habitat degradation led to decreased stocks,threatening food security communities'dependent primary source sustenance.
Agricultural impacts include nutrient runoff contributing to eutrophication,excessive inputs leading to algal blooms,oxygen depletion,and negatively impacting ecological health.
The loss of glaciers due to global warming raises concerns about future availability,given that meltwater contributes significantly,making vulnerable changes and resulting in climate change.
In conclusion,Earth's six largest lakes face numerous environmental challenges from human activities such as dam construction,industrialization,sand dredging,decline,fish fisheries,agriculture,loss,glaciers,and global droughts warming. These challenges threaten biodiversity,ecological balance,livelihoods,and communities that depend on these freshwaters. Stakeholders must take proactive measures to mitigate adverse effects and ensure the sustainability of these vital ecosystems.
References:
1. National Geographic
2. World Wildlife Fund(WWF)
3. United Nations Environment Programme(UNEP)
===========================================================
The Five Largest Rivers Worldwide
The Earth's five most significant rivers are the Amazon,the Nile,the Yangtze,the Mississippi,and the Ganges. These rivers are vital in supporting ecosystems,agriculture,and human populations. However,human activities such as dams,industrialization,dredging sand,and global warming have led to numerous challenges for these rivers and their surrounding environments.
1. The Amazon River
The Amazon River is the largest in the world by volume and discharge,spanning over 6,400 kilometers(4,000 miles). The river flows through Brazil,Colombia,Peru,and other South American countries. It is home to many species,including over 3,000 fish species,making it an essential food source and income for millions.
Dams and industrialization have caused significant harm to the Amazon River. Dams have been constructed to generate hydroelectric power,but they have also disrupted the river's natural flow,affecting fish migration and habitat. Industrial activities,such as deforestation and mining,have led to pollution,which has caused the death of fish and fisheries in the river.
2. The Nile River
The Nile River is the longest in the world,stretching approximately 6,650 kilometers(4,130 miles)from Central Africa to the Mediterranean Sea. The river is a vital water source for millions of people and plays a significant role in agriculture,particularly Egypt.
Industrialization and population growth have put immense pressure on the Nile River. Pollution from industries and agricultural runoff has led to the death of fish and aquatic life in the river. Dams and water diversion projects have also affected the river's natural flow,causing a decline in water levels and negatively impacting agriculture and ecosystems.
3. The Yangtze River
The Yangtze River is the longest in Asia,spanning over 6,300 kilometers(3,900 miles)through China. It is an essential water source for agriculture,industry,and human consumption. The Yangtze River Basin is home to over 400 million people,making it one of the most densely populated areas in the world.
The construction of the Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River has led to significant changes in the river's ecosystem. The dam has caused habitat loss for numerous species,including fish and other aquatic life. Additionally,the reservoir created by the dam has led to the death of agriculture and the submergence of ancient cultural sites.
4. The Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river in the United States,spanning over 3,700 kilometers(2,300 miles)from the Rocky Mountains to the Gulf of Mexico. The river is a critical source of water and nutrients for the surrounding ecosystems and agriculture.
Dams,dredging,and pollution have affected the Mississippi River and its surrounding areas. Dams have disrupted the river's natural flow,impacting fish migration and habitat. Dredging has removed valuable sediment from the river,leading to erosion and the loss of wetlands. Industrial pollution has contributed to the death of fish and other aquatic life in the river.
5. The Ganges River
The Ganges River,also known as the Ganga,is one of the most sacred rivers in India and flows through India and Bangladesh. The river is vital for agriculture,human consumption,and religious practices.
Dams,pollution,and global warming have caused severe challenges for the Ganges River. Dams have disrupted the river's natural flow,impacting fish migration and habitat. Pollution from industries,agriculture,and human waste has led to the death of fish and aquatic life. Global warming has contributed to the decline of glaciers in the river's headwaters,impacting water availability downstream.
In conclusion,the Earth's five largest named rivers face numerous challenges due to human activities and global warming. These challenges include the death of fish and fisheries,the death of agriculture,and the loss of natural habitats. Addressing these issues and implementing sustainable practices to protect these vital rivers and their ecosystems is essential.
References:
1."Dams and the Amazon River:Environmental Impacts and Solutions"-This reference provides an in-depth analysis of the environmental impacts of dams on the Amazon River,including the effects on fish migration,habitat,and aquatic life.
2."The Nile:A River in Crisis"-This reference discusses the various challenges faced by the Nile River,including pollution,water scarcity,and the impact of dams and water diversion projects on the river's ecosystems.
3."The Yangtze River:Environmental Challenges and Opportunities"-This reference examines the environmental challenges faced by the Yangtze River,including the impacts of the Three Gorges Dam,pollution,and biodiversity loss.
4."The Mississippi River:Dams,Dredging,and Environmental Impacts"-This reference explores the environmental impacts of dams,dredging,and pollution on the Mississippi River and its surrounding ecosystems.
5."The Ganges River:Challenges and Solutions for a Sacred River"-This reference discusses the challenges faced by the Ganges River,including pollution,global warming,and the impacts of dams on fish migration and habitat.
=================================================================================
Impact of Dams,Industrialization and Over-Fishing on the Mekong River
The Mekong River,which spans six Southeast Asian countries,has been significantly impacted by the construction of numerous dams. These dams have led to the death of water quality,fish,and fisheries and threatened the very existence of the river itself. Factors such as global warming,China's dams,and industrialization have contributed to this bleak future for the Mekong River and its surrounding communities.
## List of Countries with Dams on the Mekong River
1. Laos
2. Cambodia
3. Thailand
4. Myanmar
5. Vietnam
6. China
The construction of dams in these countries has led to the alteration of the river's natural flow,causing detrimental effects on the environment and local communities.
## Death of Water Quality
Dams have resulted in a decrease in water quality in the Mekong River. The reservoirs created by thesedamstrap sediments and pollutants,which can lead to the eutrophication of the water. This process,in turn,depletes oxygen levels in the water,making it difficult for aquatic life to survive. Additionally,the construction of dams has caused the release of toxic chemicals into the river,further exacerbating the water quality issue.
## Death of Fish and Fisheries
The construction of dams on the Mekong River has led to the death of fish and fisheries. By blocking the natural migration of fish,dams disrupt the reproductive cycles of these species,leading to a decline in their populations. This decline has significantly impacted the livelihoods of local communities,who rely on fishing as a primary source of income.
## Death of the River Itself
The construction of dams on the Mekong River has led to the death of the river itself,as it alters the natural flow of the water. This alteration can result in the loss of vital ecosystems and habitats and the disruption of sediment transportation,which is essential for the maintenance of the river's banks and channels.
## Global Warming
Global warming has exacerbated the effects of dams on the Mekong River. Rising temperatures have led to increased evaporation rates in the reservoirs,reducing water availability for downstream communities. Additionally,global warming has contributed to more frequent and severe droughts,which can further stress the river's ecosystems and reduce water availability.
## China's Dams
China's dams on the Mekong River have played a significant role in the decline of the river's health. These dams have altered the river's natural flow and contributed to decreased water quality and fish populations. China's dams have also caused the release of toxic chemicals into the river,further exacerbating the water quality issue.
## Industrialization
Industrialization in the Mekong River basin has also contributed to the decline of the river's health. Increased industrial activity has led to the release of pollutants and waste into the river,further degrading water quality and impacting the health of aquatic life.
## Bleak Future
The future of the Mekong River looks bleak due to the continued construction of dams,global warming,and industrialization. These factors have led to declining water quality,fish populations,and overall river health.”
References:
1. Mekong River Commission(www.mrcmekong.org)
2. International Union for Conservation of Nature(www.iucn.org)
3. World Wildlife Fund(www.worldwildlife.org)
Feds call for water cutbacks as Colorado River is in 23-year ...
https://www.cnbc.com›2022/08/17›feds-call-for-wat...
3 days ago—A 23-yeardroughthas beendrying upthe ColoradoRiverand the effectsofclimate change,both in termsofextremeheatand low ...
Rio Grande runs dry in Albuquerque for the first time in 40 years
https://www.washingtonpost.com›rio-grande-drought
Jul 22,2022—Thedrying of theRio Grande comes as the summer's hotter and drier weather has fueleddroughtand fire throughout the West.
Colorado River drought:A US climate disaster to ...-Grid News
https://www.grid.news›story›climate›2022/07/25›th...
Jul 25,2022—The ColoradoRiverisdying. The water source for 40 million people across sevenstatesand partofMexico is rapidlydrying out, ...
Current Map|U.S. Drought Monitor-University of Nebraska ...
https://droughtmonitor.unl.edu
The maps,which are based on analysisof thedata,are released each Thursday at 8:30 a.m. Eastern Time. Intensity and Impacts. None;D0(AbnormallyDry) ...
https://www.news4jax.com›weather›2022/06/27›lo...
Jun 27,2022—AllofFlorida'sgroundwateris replenished by rainfall which is in short supply recently. Duval County is more than 5 inches below normal for ...
Texas is drying up. We better protect our groundwater.
https://blogs.edf.org›waterfront›2022/07/20›texas-...
Jul 20,2022—According to theU.S.Drought Monitor,more than 80%ofTexas has been facing drought conditions mostofthe year. Extreme or worse drought ...
'Major Aquifers in Trouble'as Western U.S. Adapts to Water ...
https://www.theenergymix.com›news
Feb 11,2022—Bessiresays far moregroundwateris being pumpedoutthan can be replenished,and mostdry-areaaquifersare disappearing,including two ...
As the climate dries the American west faces power and water ...
https://www.unep.org›news-and-stories›story›clim...
Aug 2,2022—Lake Mead,in Nevada and Arizona,and Lake Powell,in Utah and Arizona,are currently at their lowest levels ever.'Dead pool'status would mean ...
Climate Change Articles